Grade 8 Science: Galapagos Islands
Grade 8 Science: Galapagos Islands


1: Plants/Animals Inhabited First
Correct Responses
-
PLANTS with an explanation based plants being able to make their own
food (photosynthesis).
- Examples:
- Plants can photosynthesize.
-
PLANTS with an explanation based only on survival OR mode of transportation
of plants/animals. [Photosynthesis or making food not explicitly mentioned.]
- Examples:
- They could survive there first because plants only need water
and air.
- Without plants there would not be animals.
- First the plants arrived. Then the animals can come and survive by
eating the plants.
- Seeds could just be carried by the wind. Animals would have to swim
a long distance.
- Seeds from South America blew to the islands.
-
ANIMALS with a reasonable explanation based on transportation AND availability
of alternative food sources (may be implicit based on the specific
type of animal named).
- Examples:
- Birds could fly over to the island to nest and survive by
eating fish from the sea.
- Seals can swim there and live on the rocky shore. [Assumes seals eat
fish.]
Incorrect Responses
-
PLANTS with no explanation or an incorrect explanation. [May include
a correct statement that does not apply to the situation.]
- Examples:
- They just grew from the ground.
- Because plants grow faster and live longer.
- They are living organisms.
- Plants were on Earth before animals.
-
ANIMALS with no explanation or an incorrect explanation.
- Examples:
- Birds could just eat the seeds in the ground.
- They are everywhere.
- There will be a surplus of food.
- Animals can move but plants cannot.
- Animals migrate.
- Other incorrect
Grade 8 Science: Galapagos Islands


2A: Effect of Cats
Correct Response
-
Refers to cats preying upon other organisms, or similar (resulting in a reduction
in population).
- Examples:
- They might pass on diseases to other animals.
- The cats help them by eating the rats and mice.
- Their prey could become extinct.
Incorrect Responses
-
Refers only to an effect on the cat with no explicit effect on other organisms.
- Examples:
- They cannot survive on the island.
- Cats might reproduce and get
out of control.
- Other incorrect
2B: Effect of Goats
Correct Responses
-
Refers only to the goats eating plants (resulting in a reduction of the amount
of plant life on the island).
- Examples:
- Large pieces of grass will disappear as the goats eat it.
- It could lead to erosion if the goats clear the land by eating all
the plants.
-
Refers to an effect of the goat on other animals (e.g., competition for food/habitat,
as a food source for predators, etc.). [Note: may also refer to the goats
eating plants.]
- Examples:
- The animals that eat goats would have more food.
- They might become a source of food.
- The goats will eat up the plants and the populations that depend on
plants will decrease.
Incorrect Responses
-
Refers only to an effect on the goat with no explicit effect on other organisms.
- Examples:
- Goats would have more babies.
- They would die because they don’t have any food.
- Other incorrect
Grade 8 Science: Galapagos Islands
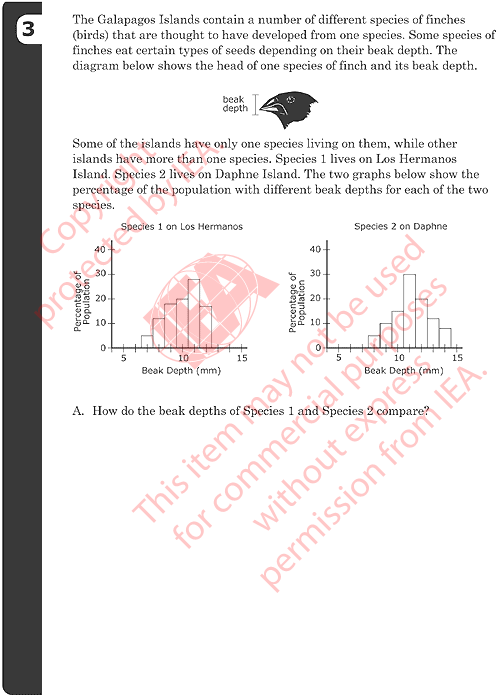
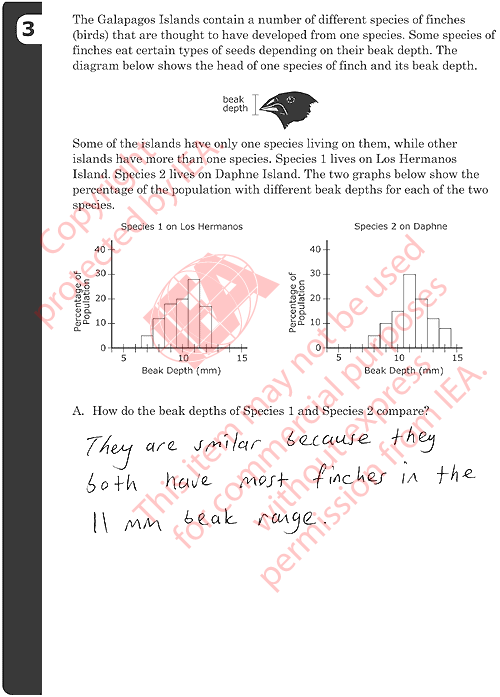
3A: Description of Beak Sizes
Correct Responses
-
Gives a description based on similarities that is supported with information
in the graphs.
- Examples:
- Both are similar in average beak size.
-
Gives description based on differences that is supported with information
in the graphs.
- Examples:
- Species 1 is a little bit shorter than Species 2.
- Species 2 has more that are big.
- Species 2 has a wider range of depth than of Species 1.
-
Give a description that includes both similarities and differences.
- Examples:
- Both species have the greatest amount of birds with 11mm
beak depths, but Species 1 does not have birds with beak
depths bigger than 13mm.
Incorrect Responses
-
States only that the two species are the ‘same’ or ‘similar’ without
supporting information from the graphs.
- Examples:
- They are nearly the same.
-
States that one species is larger or smaller than the other, but does
not identify which.
- Examples:
- One of them is a bit different on beak depth.
- Other incorrect
Grade 8 Science: Galapagos Islands
3B: Types of Seeds Eaten
Correct Responses
-
States that the two species eat the same (similar) types of seeds.
[Response to A indicates that the two species have the same or similar size
beaks.]
-
States that Species 2 eats larger seeds than Species 1. [Response to
A indicates that Species 2 is larger.]
-
States only that birds (finches) with larger beaks eat larger seeds
(or similar). [No explicit comparison of the two species.]
Incorrect Responses
-
States that the two species eat the same (similar) types of seeds,
but this conclusion is inconsistent with the response given in Part A.
-
States that one species eats larger seeds than the other, but this
conclusion is inconsistent with the response given in Part A.
- Other incorrect
Grade 8 Science: Galapagos Islands
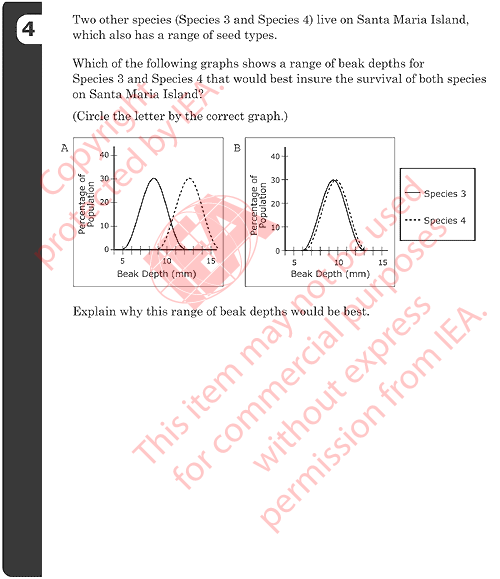
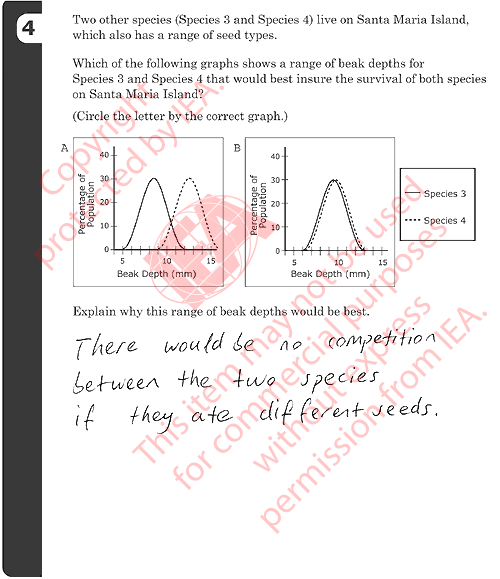
4: Graphs of Beak Depths for Species 3 and 4
Correct Response
- A with an explanation that relates the difference in beak size to reduced competition (or similar).
- Examples:
- With the different sized beaks they would not have to share food.
- One species will eat the small seeds and one will eat the large seeds.
- They each have their own food source.
Partial Response
- A with a minimal explanation that refers only to the difference in beak size. [Does not explicitly mention competition for seeds or similar.]
- Examples:
- Because they are different sizes.
- Because Species 3 has a smaller beak size.
Incorrect Responses
- A with no explanation or an incorrect explanation.
- Examples:
- Because their beaks look sharper.
- Because both species have a large beak to the percentage of population.
- It’s like the other graphs.
- B with no explanation or an incorrect explanation.
- Examples:
- Bigger beak depths so they could eat more seeds.
- Both are nearly equal and are a more normal size.
- It ’s better if they are the same size because they eat the same seeds.
- Other incorrect
|
|
© 2008 International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA)